Background
A 22 year old male presented with abdominal pain. CT angiography of abdomen revealed a well defined lobulated exophytic lesion arising from left lobe of liver measuring 18 x 12 cm, showing early arterial enhancement. Serum AFP: 2.9ng/ml. Biopsy from liver.
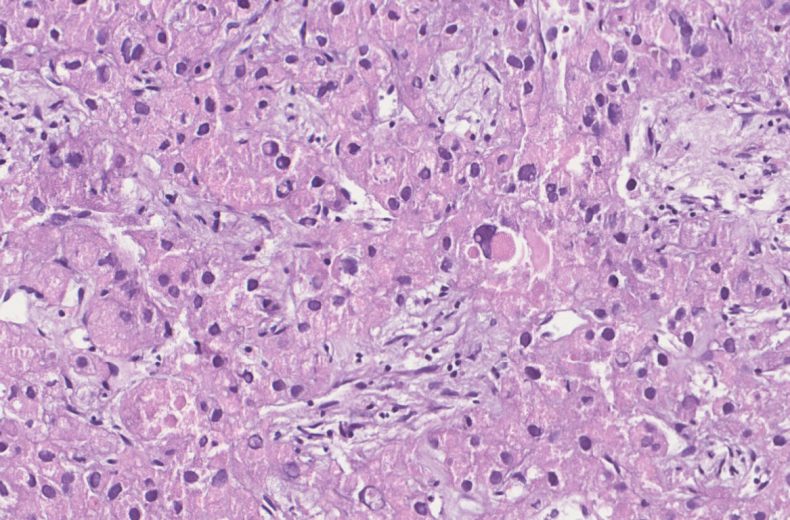
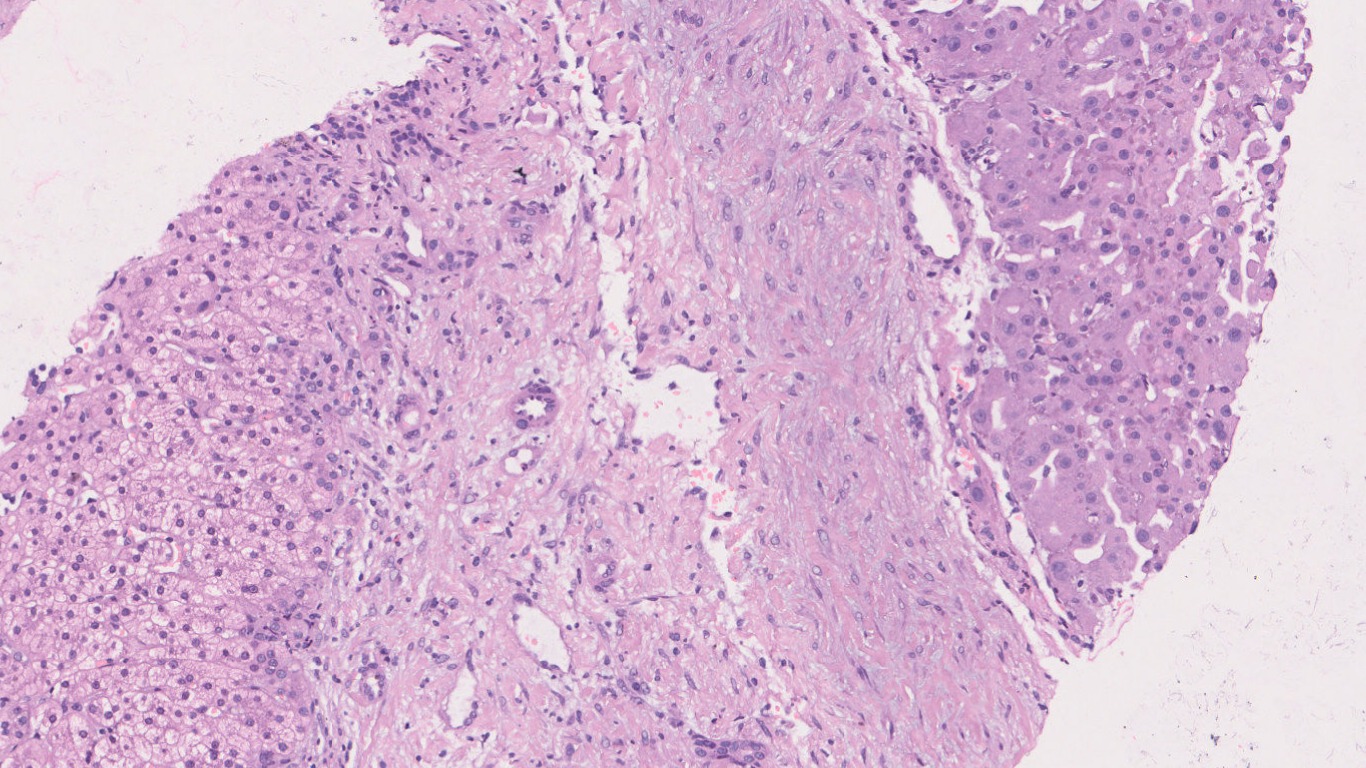
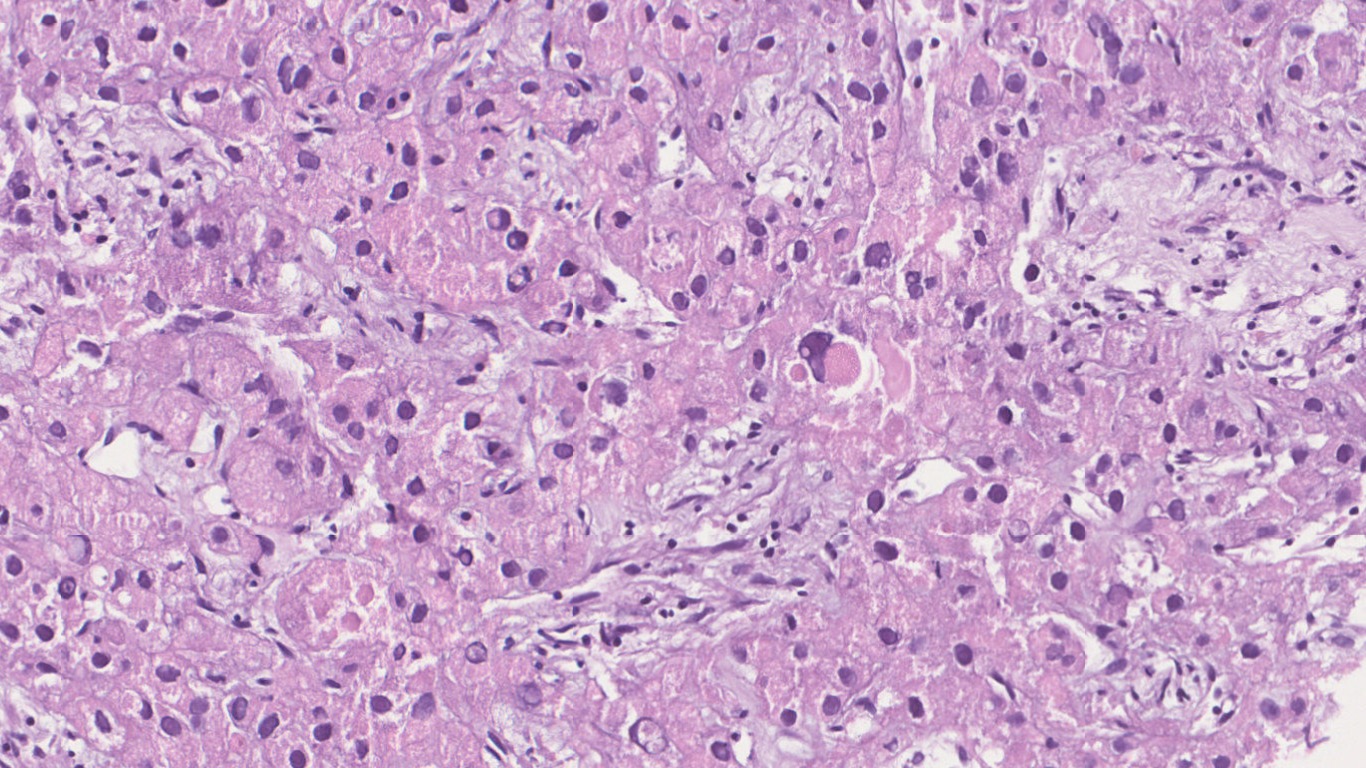
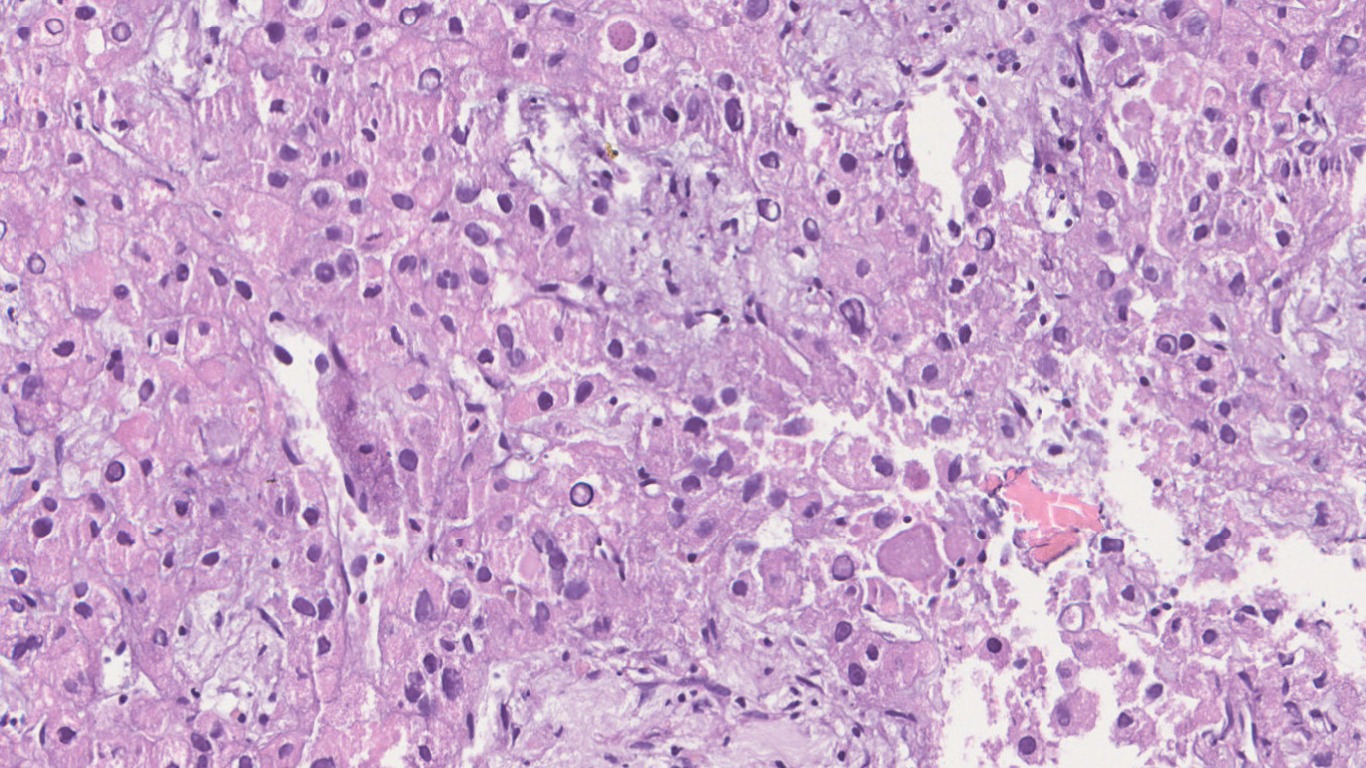
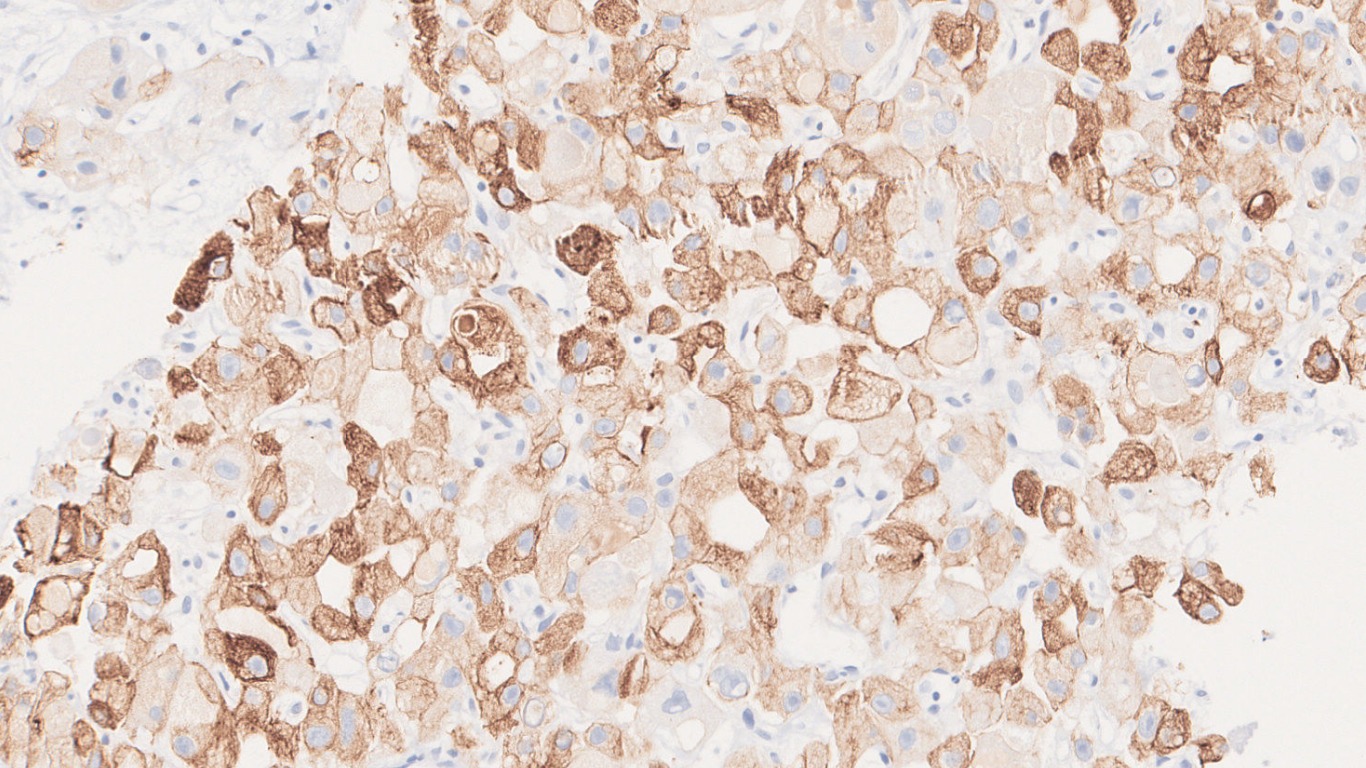
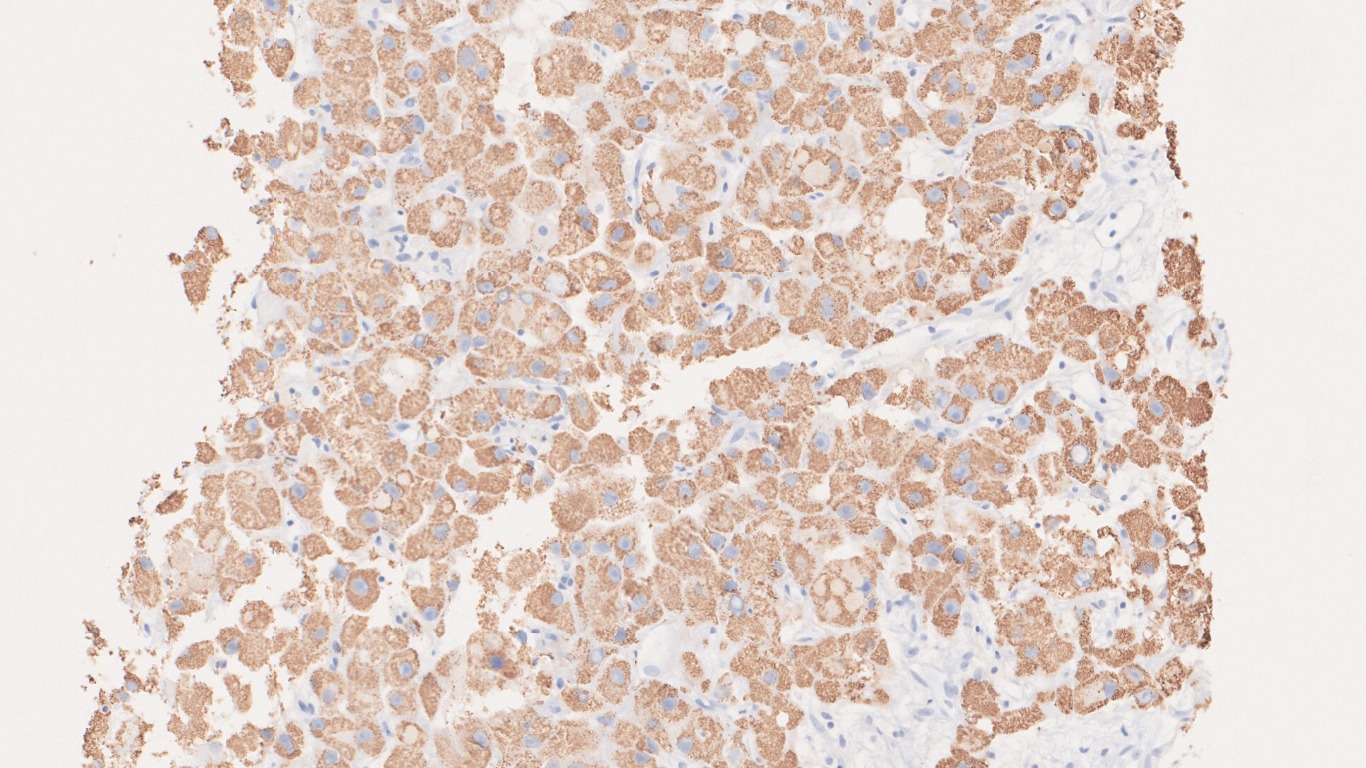
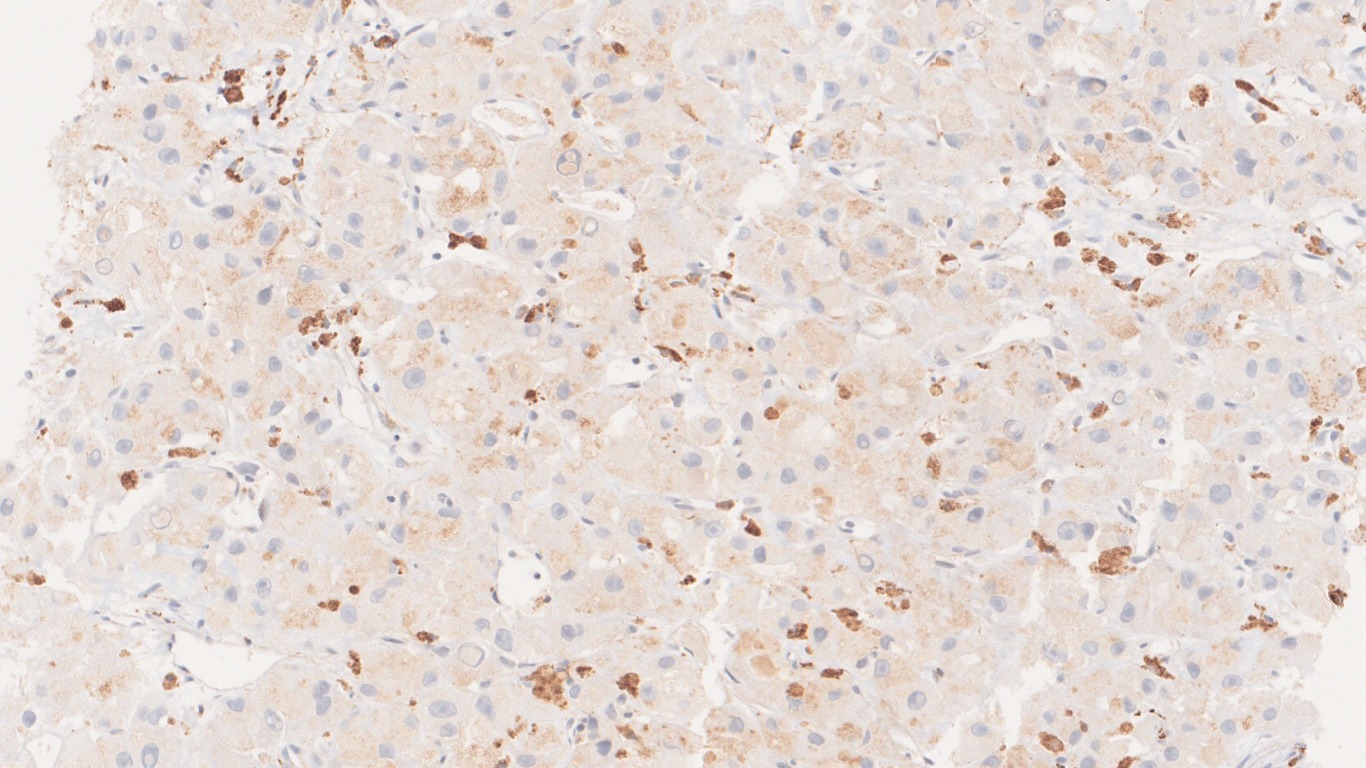
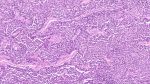
Microscopy
Questions & Answers:
- What is your diagnosis?
- Hepatocellular carcinoma- Classic
- Fibrolamellar HCC
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- Cirrohotic liver
- Which of the following findings are expected in the background liver, in this case?
- Viral hepatitis
- Steatosis
- Cirrhosis
- Normal liver
- Which of the following genetic change is diagnostic of this tumor?
- TP53
- β-catenin
- DNAJB1-PRKACA fusion
- All
- None
- Occurs in non cirrhotic liver in young adults
- More common in females
- Serum AFP levels are normal
- 60-70% cases are solitary but multiple tumors in form of satellite lesions are known.
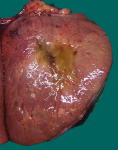
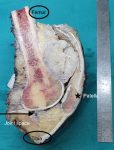
- Grossly:
- Often well circumscribed but unencapsulated lobulated mass
- Central scar can be present but does not show enhancement on CT
- Differential Diagnosis:
- Classic hepatocellular carcinoma
- Focal nodular hyperplasia
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- Metastatic carcinoma
- Immunohistochemistry:
- Positive stains: CK7, CD68, HepPar-1, CEA, Glypican-3
- Negative stains: p53 and β-catenin
- Molecular hallmark:
- Del 19 leading to formation of DNAJB1-PRKACA fusion transcript
- Treatment and prognosis:
- Aggressive tumor
- However, several studies have shown better outcome in these patients than classic HCC
- Excision is treatment of choice
- When resection is not possible, liver transplantation remains the only option.
Contributed by: Dr. Garima Durga
Compiled by: Dr Himanshi Diwan
In case of queries, email us at: kumar.ankur@rgcirc.org
Fibrolamellar HCC HCC Hepatocellular carcinoma Liver Neoplasms
Last modified: 29/07/2021